Rancidity: Why Do Foods Turn Rancid?
Rancidity refers to the complete or incomplete hydrolysis or oxidation of fats and oils when exposed to air, light, moisture, and bacterial activity; this generally occurs in food items, making them undesirable for consumption. In more general terms, rancidity is always associated with food products that contain oil and fatty acids. Fatty acids are nothing but fats, cholesterol, and steroids. Rancidity reactions typically occur in three steps: initiation, propagation, and termination. At the end of rancidification, fats, oils, and other lipids are decomposed, thus forming highly reactive molecules. These are responsible for the unpleasant smell and taste of rancid foods. In some cases, rancidification may also lead to the loss of vitamins in food.
Tags
Comments
Leave a Comment
Comments are loading... If you don't see any, be the first to comment!
Related Videos
Understanding Fats
Visual Learning Systems
Understanding Fats
Owner - Visual Learning Systems - Powered By Boclips
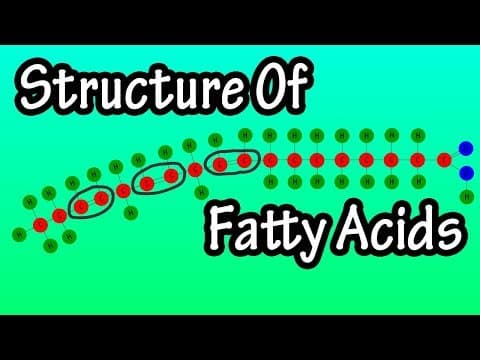
Fatty Acids - What Are Fatty Acids - Structure Of Fatty Acids - Types Of Fatty Acids
Owner - Whats Up Dude
Carnitine Biosynthesis Pathway
JJ Medicine

This Is How Your Skin Holds In Bodily Fluids
KidzSearch

Fats - Types Of Fats - What Is Saturated Fat - What Is Unsaturated Fat - Omega 3's And Omega 6s
Owner - Whats Up Dude
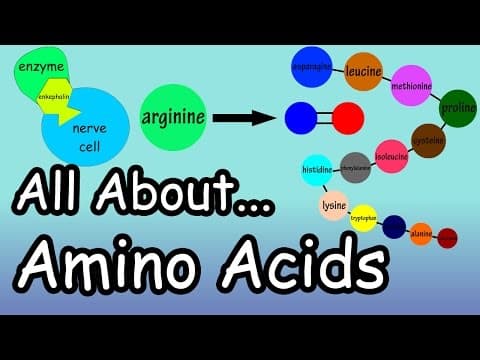
Amino Acids - What Are And What Do Amino Acids Do - What Are Complete And Incomplete Proteins
Owner - Whats Up Dude

Health benefits of eggs - Ask Coley - Health Tips for Kids | Educational Videos by Mocomi
Owner - MocomiKids

What are fats?
Owner - Smile and Learn - English
Omega-3: Healthy Fat?
Imagine Learning - Twig (middle years+)
